01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
package algs13;
import stdlib.*;
public class XFixedCapacityStackOfStrings {
private String[] a; // holds the items
private int N; // number of items in stack
// Invariant (after the constructor):
// a[0]..a[N-1] are non null
// a[N]..a[a.length-1] are null
public XFixedCapacityStackOfStrings (int capacity) {
this.a = new String[capacity];
this.N = 0;
}
public int size () { return N; }
public boolean isEmpty () { return (N == 0); }
public void push (String item) {
if (item == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException ();
if (N >= a.length) throw new RuntimeException ("Stack full");
a[N] = item;
N++;
}
public String pop () {
if (N <= 0) throw new RuntimeException ("Stack empty");
N--;
String result = a[N];
a[N] = null;
return result;
}
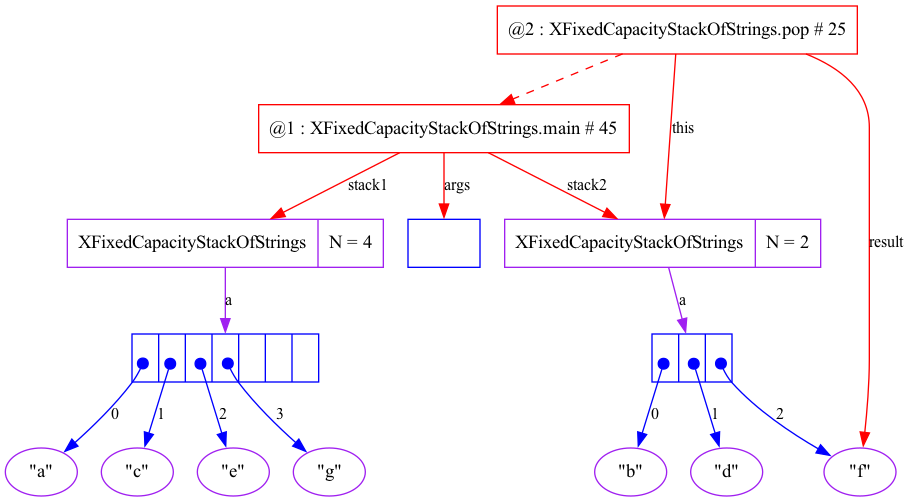
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Trace.showObjectIdsRedundantly (true);
Trace.showBuiltInObjects(true);
//Trace.drawStepsOfMethod ("main");
Trace.drawSteps ();
Trace.run ();
XFixedCapacityStackOfStrings stack1 = new XFixedCapacityStackOfStrings (7);
XFixedCapacityStackOfStrings stack2 = new XFixedCapacityStackOfStrings (3);
stack1.push ("a");
stack2.push ("b");
stack1.push ("c");
stack2.push ("d");
stack1.push ("e");
stack2.push ("f");
stack1.push ("g");
while (!stack2.isEmpty()) {
StdOut.println (stack2.pop ());
}
StdOut.println();
while (!stack1.isEmpty()) {
StdOut.println (stack1.pop ());
}
}
}
|